Right now, the version of Hyper-Text Markup Language supported in browsers far and wide is HTML 4. The next version is on the way; the World Wide Web Consortium is working on the next version of the markup language to enhance the performance of web pages. In this article, let’s look at the details of HTML 5.
HTML is a group of web technologies, primarily including the markup scheme itself, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and a scripting language (most commonly used is JavaScript). The markup scheme mentioned here is for creating elements within a web page so that the browser knows what to display and where. The CSS part is for showing the elements their formatting—color, text size, font, and such other stuff. The scripting language is for creating user-executable code that the browser can interpret and present to the end users.
So far, HTML went through four major revisions. Minor revisions are always happening and popular browsers incorporate the available new standards so that they can display web pages more effectively. The latest revision, the fifth version of HTML is still under development, and not many browsers support it fully.
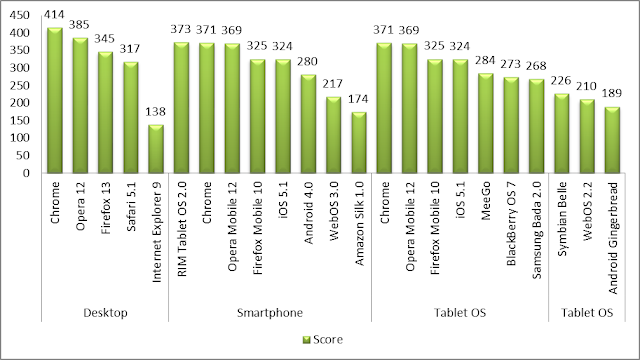
Here is the statistic of browser scores based on support for HTML 5. The greater the score, the better it is.
As you can see Google Chrome scores much better than others. It’s an open-source browser under constant development, just like Mozilla Firefox, and hence, the browser incorporates the new developments faster. On the other hand, Internet Explorer doesn’t provide any noticeable support for HTML 5.
So far you have seen the advancement of online video sites, audio sites, multimedia-rich content, and interactive programs like games online. All of this happened due to the presence of proprietary technologies like Flash, QuickTime, or Silverlight created by individual companies.
You probably know all the fuss about how insecure Adobe Flash really is. It is one of the most downloaded and used programs in the Internet. And yet, the most popular smartphone—Apple iPhone—or any Apple product at that matter, does not support Flash. Why is it so? It is because Flash could make your system highly insecure. It has a number of vulnerabilities which could be exploited pretty easily to run malicious scripts on your computer.
Flash is a very important plugin for all the browsers as without it, you cannot play online videos and most of the games. How can you rely on insecure technologies like this for the future? This is one of the reasons why HTML 5 is most welcome. This new version of the markup language will replace Flash and such other technologies for displaying online video and games.
With HTML 5, you can do the following:
Aren’t these reasons enough to have HTML 5 evolve the way it does?
You probably have already seen web-based applications for image editing, movie creation, animation, and video chatting. All or most of them use proprietary technologies that more or less could be insecure. But with the evolution of HTML 5, all of that will be possible without the use of any external piece of software such as a browser plugin. This will enhance the security of your browser greatly.
As you have seen already, Chrome supports HTML 5 greatly. Over 80 per cent of the features of the language are available in Chrome, while Internet Explorer, the third most popular browser, supports less than 30 per cent of what is offered by HTML 5. This is reason enough to switch browsers, isn’t it?
Also, it more or less seems like Microsoft has lost all hopes for Internet Explorer. Even the version 10 of the browser doesn’t say a lot about better support for HTML 5. Instead, it has better support for Flash (what a foolish thing to do, one might wonder!). According to Microsoft, the IE 10 will support HTML 5 for the future web and Flash for websites that still rely on the past technologies, thus giving better support for everything out there! However, if you research further, you know that the support for HTML 5 is only around 50 per cent of the standard, which is still far less than any other browser out there.
This is the age of Chrome, and that browser has become one of the most popular very quickly. Even Mozilla Firefox couldn’t stop Chrome. For a better browser experience with the latest website designs and technologies, you should ideally use Google Chrome.
HTML 5 as you can see will pave way for a more secure future. The websites will turn interactive in a far greater sense. You will be able to incorporate hardware support and multimedia features into your websites without having to do a lot of work. All the specifications and support are available right from W3C website.
What Is HTML?
HTML is a group of web technologies, primarily including the markup scheme itself, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and a scripting language (most commonly used is JavaScript). The markup scheme mentioned here is for creating elements within a web page so that the browser knows what to display and where. The CSS part is for showing the elements their formatting—color, text size, font, and such other stuff. The scripting language is for creating user-executable code that the browser can interpret and present to the end users.
So far, HTML went through four major revisions. Minor revisions are always happening and popular browsers incorporate the available new standards so that they can display web pages more effectively. The latest revision, the fifth version of HTML is still under development, and not many browsers support it fully.
Here is the statistic of browser scores based on support for HTML 5. The greater the score, the better it is.
As you can see Google Chrome scores much better than others. It’s an open-source browser under constant development, just like Mozilla Firefox, and hence, the browser incorporates the new developments faster. On the other hand, Internet Explorer doesn’t provide any noticeable support for HTML 5.
Why HTML 5?
So far you have seen the advancement of online video sites, audio sites, multimedia-rich content, and interactive programs like games online. All of this happened due to the presence of proprietary technologies like Flash, QuickTime, or Silverlight created by individual companies.
You probably know all the fuss about how insecure Adobe Flash really is. It is one of the most downloaded and used programs in the Internet. And yet, the most popular smartphone—Apple iPhone—or any Apple product at that matter, does not support Flash. Why is it so? It is because Flash could make your system highly insecure. It has a number of vulnerabilities which could be exploited pretty easily to run malicious scripts on your computer.
Flash is a very important plugin for all the browsers as without it, you cannot play online videos and most of the games. How can you rely on insecure technologies like this for the future? This is one of the reasons why HTML 5 is most welcome. This new version of the markup language will replace Flash and such other technologies for displaying online video and games.
With HTML 5, you can do the following:
- HTML 5 incorporates online multimedia without the need for plugins like Flash and Silverlight.
- It will enable browsers to use the hardware features of your computer—web cam, microphone, speakers, etc.
- It will enable multi-touch on web content—for instance, it will incorporate touch-zooming on images and videos better than how browsers incorporate it today.
- It will incorporate animations without using any external technology like Flash—a standalone browser installation will play 2D and 3D animations.
- As smart TVs are also becoming popular, HTML 5 support on their browsers will enable playing online video and games directly from them.
Aren’t these reasons enough to have HTML 5 evolve the way it does?
You probably have already seen web-based applications for image editing, movie creation, animation, and video chatting. All or most of them use proprietary technologies that more or less could be insecure. But with the evolution of HTML 5, all of that will be possible without the use of any external piece of software such as a browser plugin. This will enhance the security of your browser greatly.
Browser Support
As you have seen already, Chrome supports HTML 5 greatly. Over 80 per cent of the features of the language are available in Chrome, while Internet Explorer, the third most popular browser, supports less than 30 per cent of what is offered by HTML 5. This is reason enough to switch browsers, isn’t it?
Also, it more or less seems like Microsoft has lost all hopes for Internet Explorer. Even the version 10 of the browser doesn’t say a lot about better support for HTML 5. Instead, it has better support for Flash (what a foolish thing to do, one might wonder!). According to Microsoft, the IE 10 will support HTML 5 for the future web and Flash for websites that still rely on the past technologies, thus giving better support for everything out there! However, if you research further, you know that the support for HTML 5 is only around 50 per cent of the standard, which is still far less than any other browser out there.
This is the age of Chrome, and that browser has become one of the most popular very quickly. Even Mozilla Firefox couldn’t stop Chrome. For a better browser experience with the latest website designs and technologies, you should ideally use Google Chrome.
Conclusion
HTML 5 as you can see will pave way for a more secure future. The websites will turn interactive in a far greater sense. You will be able to incorporate hardware support and multimedia features into your websites without having to do a lot of work. All the specifications and support are available right from W3C website.