QR code is a type of two dimensional code. Haven’t you seen barcodes on products that you purchase from a supermarket? These one dimensional codes contain a small bit of information identifying the particular product. They are called UPC (Universal Product Code). These codes can contain only a limited amount of info up to 20 characters or so. When information such as a website address, a small text description, an image, etc., had to be stored, we needed better barcodes, thus the two dimensional codes came about. QR code, also known as Quick Response code, is one of the most widely used 2-D codes.
QR code was invented by a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation of Japan called Denso that manufactured automobile equipment for Toyota and other manufacturers. It is interesting to note that the QR code was invented by them for quick scanning of such items as car air conditioners, windshield wipers, horns, airbags, etc.
Later on, the technology became known far and wide and manufacturers started seeing the potential of this type of marketing.
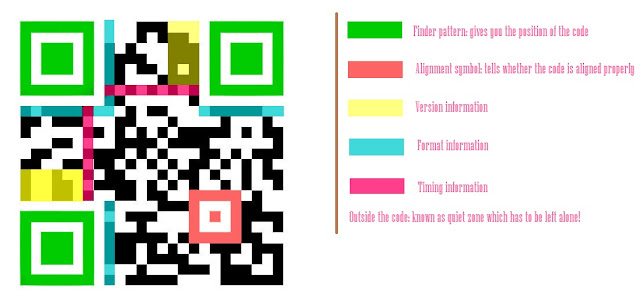
Here is a QR code with information about various parts of it:
If you have a company that supplies various products that consumers can purchase, you can set up a mobile ‘experience’ website for your customers and you can print QR code tags to be attached to your products. You can encode the URL of your mobile website into this code, so that when a customer scans the code he is taken to your website, thereby enabling him to get more information about the product and possibly place an order.
This particular form of marketing could become highly successful and convenient for targeting window-shoppers. You can supply QR code tags on fliers, TV ads, wallpapers, brochures, etc., so that they are accessible to a wide range of people.
Most of the manufacturers today, however, are using QR codes and such other 2-D codes just to take the customer to a website that offers no compatibility to the handheld device the customer has.
A QR code reader is available for all sorts of operating systems—Symbian, Apple iOS, Android, Windows Phone, etc., and most of the customers are using a handheld device such as a tablet or a smartphone to scan QR codes. They are looking for a website optimized for their smartphone. If you take them to a regular website, it is not going to help the particular customer.
I have seen most of the QR codes found on products out there taking customers to unnecessary places making it difficult for them to even learn about the product let alone order it. This practice would eventually only help kill the QR code marketing strategy.
Another important use of QR codes is in tracking the popularity of your advertisement campaigns. Unlike the regular TV ads and product brochures, QR code campaigns can be tracked extensively. Once a customer scans a QR code that you publish, he is taken to a specific website, and everything the customer does on the particular website to whether he has made a purchase or not, can be tracked and imported into customer research database. This in turn will fine-tune your marketing campaigns.
You can generate and scan QR codes using your mobile phone despite which operating system it is using—Android, Apple iOS, or Windows Phone. Major apps include Google Goggles, Nokia Barcode Reader, Microsoft Tag, QR Droid, and a number of others.
You can create your own QR codes as well as read the ones found on various products using these scanners.
Another important concern of QR code is its security. There have been instances of mobile phone hacking through infected QR codes. Kaspersky Lab has reported the cases extensively, causing panic among smartphone users. A recent QR code attack that happened in Russia diverted users who thought they were scanning a legitimate code, to an SMS application that sent text messages to premium-rate numbers making money for the attacker.
This happens because the QR code that was read contained wrong URL that redirected the phone to the virus site. This is just like you typing in the URL of a virus site on your browser’s address bar and navigating to it. Normally you won’t do it if you suspect the URL, but looking at the QR code you cannot say what URL it contains, can you? After you scan it, it is the scanner that does all the work, and you know the scanners are dumb!
As long as you have proper security installed on the system, you should be able to browse without fear.
If used wisely, QR codes could mean extreme business success as they are convenient for both customers and product manufacturers. They can store a huge amount of information, much more than the regular barcodes—UPC and EAN—can contain. However, as always, security could be an issue and you should be sure if you are scanning the correct QR code or not. As smartphones and tablets become more and more ubiquitous, security also becomes a major issue.
[Image credit: Denso]
QR code was invented by a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation of Japan called Denso that manufactured automobile equipment for Toyota and other manufacturers. It is interesting to note that the QR code was invented by them for quick scanning of such items as car air conditioners, windshield wipers, horns, airbags, etc.
Later on, the technology became known far and wide and manufacturers started seeing the potential of this type of marketing.
Here is a QR code with information about various parts of it:
Implementation of QR Codes
If you have a company that supplies various products that consumers can purchase, you can set up a mobile ‘experience’ website for your customers and you can print QR code tags to be attached to your products. You can encode the URL of your mobile website into this code, so that when a customer scans the code he is taken to your website, thereby enabling him to get more information about the product and possibly place an order.
This particular form of marketing could become highly successful and convenient for targeting window-shoppers. You can supply QR code tags on fliers, TV ads, wallpapers, brochures, etc., so that they are accessible to a wide range of people.
Most of the manufacturers today, however, are using QR codes and such other 2-D codes just to take the customer to a website that offers no compatibility to the handheld device the customer has.
A QR code reader is available for all sorts of operating systems—Symbian, Apple iOS, Android, Windows Phone, etc., and most of the customers are using a handheld device such as a tablet or a smartphone to scan QR codes. They are looking for a website optimized for their smartphone. If you take them to a regular website, it is not going to help the particular customer.
I have seen most of the QR codes found on products out there taking customers to unnecessary places making it difficult for them to even learn about the product let alone order it. This practice would eventually only help kill the QR code marketing strategy.
Another important use of QR codes is in tracking the popularity of your advertisement campaigns. Unlike the regular TV ads and product brochures, QR code campaigns can be tracked extensively. Once a customer scans a QR code that you publish, he is taken to a specific website, and everything the customer does on the particular website to whether he has made a purchase or not, can be tracked and imported into customer research database. This in turn will fine-tune your marketing campaigns.
QR Code on Your Mobile Phone
You can generate and scan QR codes using your mobile phone despite which operating system it is using—Android, Apple iOS, or Windows Phone. Major apps include Google Goggles, Nokia Barcode Reader, Microsoft Tag, QR Droid, and a number of others.
You can create your own QR codes as well as read the ones found on various products using these scanners.
Infected QR Codes
Another important concern of QR code is its security. There have been instances of mobile phone hacking through infected QR codes. Kaspersky Lab has reported the cases extensively, causing panic among smartphone users. A recent QR code attack that happened in Russia diverted users who thought they were scanning a legitimate code, to an SMS application that sent text messages to premium-rate numbers making money for the attacker.
This happens because the QR code that was read contained wrong URL that redirected the phone to the virus site. This is just like you typing in the URL of a virus site on your browser’s address bar and navigating to it. Normally you won’t do it if you suspect the URL, but looking at the QR code you cannot say what URL it contains, can you? After you scan it, it is the scanner that does all the work, and you know the scanners are dumb!
As long as you have proper security installed on the system, you should be able to browse without fear.
Conclusion
If used wisely, QR codes could mean extreme business success as they are convenient for both customers and product manufacturers. They can store a huge amount of information, much more than the regular barcodes—UPC and EAN—can contain. However, as always, security could be an issue and you should be sure if you are scanning the correct QR code or not. As smartphones and tablets become more and more ubiquitous, security also becomes a major issue.
[Image credit: Denso]